The Ring of Brodgar on Orkney
The so-called "quarry" at Vestra Fiold There has been a media feeding frenzy on the subject of the Altar Stone over the past few days, arising from this article:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07652-1
Article. A Scottish provenance for the Altar Stone of Stonehenge. 2024. Anthony J. I. Clarke, Christopher L. Kirkland, Richard E. Bevins, Nick J. G. Pearce, Stijn Glorie & Rob A. Ixer. Nature 632, 15 Aug 2024, pp 570-587.
We have seen BBC coverage, media reports in all of the leading journals and news outlets, and even a Nature documentary to coincide with publication. All very carefully planned.
https://youtu.be/HerAs9RRA34?si=U0R3YAkRuiF7FLYK
So first things first: Do I believe the story told in this article, and its conclusions? In short, no. The research is very technical, but I have serious reservations about it. I do not believe that the extravagant claims made by Anthony Clarke and his colleagues including Ixer, Pearce and Bevins are adequately supported by the evidence presented.
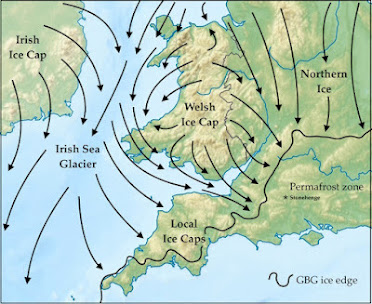
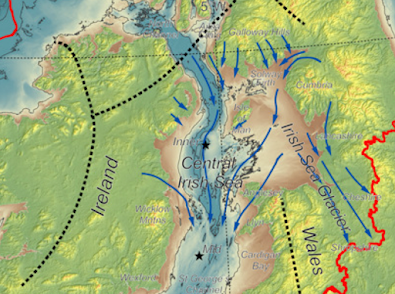
Next, I have no problems with what the authors say about ice flow directions and the likelihood of glacial erratic transport. It is indeed very difficult to conceive of ice flow conditions that might have facilitated the glacial transport of a large sandstone erratic from the ORS Orcadian Basin all the way to Salisbury Plain, via either a west coast or east coast route. As far as we know, the ice flow in the last (Devensian) Glaciation was from SE towards NW across Orkney, as described earlier on this blog.
https://brian-mountainman.blogspot.com/search?q=+Orkney+ice+flow
Source: Adrian Hall et al, 2016
This means that the erratics from Orkney would have been transported out into the North Atlantic, and there is no obvious mechanism for them to have been picked up by southward-flowing ice. That having been said, we are still in the dark about what happened in earlier glaciations, including the Anglian. It is not beyond the bounds of possibility that a large erratic of ORS sandstone from the Orcadian Basin could have been moved multiple times, during assorted glacial phases, before being transported south by the Irish Sea Ice Stream that originated off the west coast of Scotland. The abundant erratics of Ailsa Craig microgranite (from the Firth of Clyde) in West Wales confirm both the ice source and the direction of flow.
Next, what ids the quality of the geology in this paper? I await further specialist advice, but I am not very impressed.
1. The large and very elaborate piece of research may all be a complete waste of time because we do not know whether the two samples deemed to have come from the Altar Stone actually did so. They are fragments sampled by Bevins, Ixer et al, but they came out of an old box -- like many of their other samples -- and they may not have anything to do with the Altar Stone apart from having been found quite close to it.
2. That having been said, what of the other samples? There is nothing in the article about sampling protocols, but the ones deemed to be representative of the ORS sandstones of the Orcadian Basin have come from Spittal on Caithness and Cruaday on Orkney.
Cruaday Quarry on Orkney, just down the hill from Vestra Fiold, flagged up enthusiastically by archaeologists as the source for the Stones of Stenness and the Ring of Brodgar. You can see where this is leading, can't you?
https://brian-mountainman.blogspot.com/2023/04/did-vestra-fiold-quarry-provide.html
https://brian-mountainman.blogspot.com/2014/01/ring-of-brodgar-and-its-quarry.html
https://brian-mountainman.blogspot.com/2014/02/ring-of-brodgar-again.html
https://brian-mountainman.blogspot.com/2011/11/beware-quarry-hunter-on-prowl.html
It is clear to me that the authors of the current paper have taken a piece of sandstone from one of the massive grey-green sandstone beds in the hope of demonstrating that the Altar Stone came from Vestra Fiold and that it is a first cousin of the standing stones at Stenness and Brodgar. The local geology of the Stromness Sandstones according to Wikipedia:
Most of the Old Red Sandstone of Orkney is of Middle Devonian age. The lower part of the sequence, mostly Eifelian in age, is dominated by lacustrine beds of the lower and upper Stromness Flagstones that were deposited in Lake Orcadie. The two flagstones sequences are divided by the Sandwick fish bed, equivalent to the Achanarras formation of Caithness, representing an unusually persistent, deep and widespread lake that filled much of the Orcadian Basin. The sequence continues with the Rousay flagstones deposited in a similar lacustrine environment. The flagstones show a marked cyclicity in their sedimentation, with 86 such cycles being counted for the whole sequence. These are interpreted as representing regular climatically driven changes in lake level caused by Milankovitch cyclicity
The Eday Group overlies the Rousay Flagstones and represents a change to dominantly fluvial/aeolian deposition with only occasional lacustrine intervals. The Eday Group consists of three sandstone units, the lower, middle and upper Eday Sandstones separated by the Eday Flagstones and Eday Marl respectively. The Eday Marl consists mainly of red and green mudstones and siltstones and is thought to have been deposited in a river floodplain environment. Locally pseudomorphs of halite have been found and rarely marine microfossils (scolecodonts) indicating that the basin was affected by occasional marine incursions at this time.
I think we can also assume that the geologists have failed to find any sort of match between the Altar Stone samples (supposed) and the rocks of Vestra Fiold and Cruaday. If they had found a match, the banner headlines would have been even larger than they already are!
To be continued. More on the technical stuff as soon as we can manage........
====================
ABSTRACT
Understanding the provenance of megaliths used in the Neolithic stone circle at
Stonehenge, southern England, gives insight into the culture and connectivity of
prehistoric Britain. The source of the Altar Stone, the central recumbent sandstone
megalith, has remained unknown, with recent work discounting an Anglo-Welsh
Basin origin. Here we present the age and chemistry of detrital zircon, apatite and
rutile grains from within fragments of the Altar Stone. The detrital zircon load largely
comprises Mesoproterozoic and Archaean sources, whereas rutile and apatite are
dominated by a mid-Ordovician source. The ages of these grains indicate derivation
from an ultimate Laurentian crystalline source region that was overprinted by
Grampian (around 460 million years ago) magmatism. Detrital age comparisons
to sedimentary packages throughout Britain and Ireland reveal a remarkable
similarity to the Old Red Sandstone of the Orcadian Basin in northeast Scotland.
Such a provenance implies that the Altar Stone, a 6 tonne shaped block, was sourced
at least 750 km from its current location. The difficulty of long-distance overland
transport of such massive cargo from Scotland, navigating topographic barriers,
suggests that it was transported by sea. Such routing demonstrates a high level of
societal organization with intra-Britain transport during the Neolithic period.